反转链表
反转链表
题目链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/reverse-linked-list/
视频题解: https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1gE421N7W2/
# LeetCode 206. 反转链表
# 题目描述
给你单链表的头节点 head ,请你反转链表,并返回反转后的链表。
举个例子:
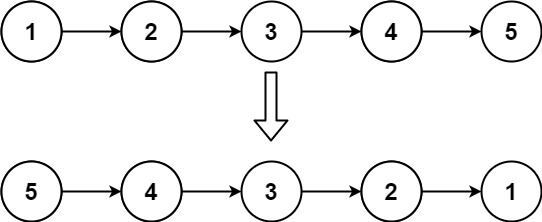
输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5]
输出:[5,4,3,2,1]
# 视频讲解
建议大家点击视频跳转到b站反转链表 (opens new window)观看,体验更佳!
# 思路解析
# 方法一 迭代法
- 定义两个指针
pre = NULL,cur = head。 - 遍历链表,当
cur不为空,就让cur指向它的前一个节点pre,然后pre和cur均向后移动一步。
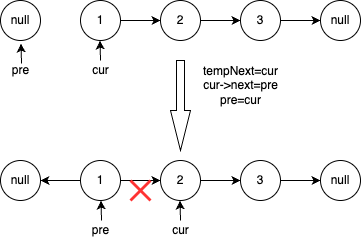
- 最终
cur == NULL,pre变成新的头节点,返回pre即可。
# C++代码
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {
if (!head)
return head;
ListNode* pre = nullptr;
ListNode* cur = head;
while (cur) {
ListNode* tmpNext = cur->next;
cur->next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = tmpNext;
}
return pre;
}
};
# java代码
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
if (head == null)
return head;
ListNode pre = null;
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
ListNode tmpNext = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = tmpNext;
}
return pre;
}
}
# python代码
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def reverseList(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
if not head:
return head
pre = None
cur = head
while cur:
tmpNext = cur.next
cur.next = pre
pre = cur
cur = tmpNext
return pre
# 方法二 递归法
递归的关键是处理好边界条件和独立子问题的划分。
这里的边界条件是对链表为空和链表只有一个节点的处理。
对head为头节点的链表进行反转 和 对head->next为头节点的链表进行反转然后在尾部加上之前的head节点 是等价的。
这里的独立子问题就是 对head->next为头节点的链表进行反转。
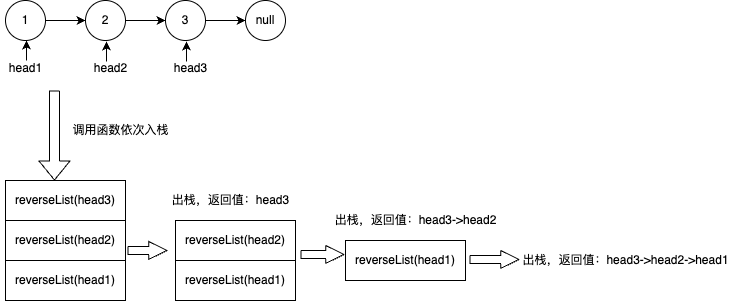
很多编程新手看到递归就比较懵,刚好借此题来讲一下递归。
递归是函数一层一层调用的过程,函数调用实际上是一个入栈出栈的过程,这里的栈就是函数调用栈,你可以用gdb调试一个程序通过bt命令来查看函数调用栈。这里的递归函数是reverseList,它的入参是链表的头节点,返回值是链表反转后新的头节点。对于链表head = [1,2,3],它的递归反转过程如下图。
# C++代码
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {
if (!head)
return head;
ListNode* newHead = head;
if (head->next) {
newHead = reverseList(head->next);
head->next->next = head;
head->next = nullptr;
}
return newHead;
}
};
# java代码
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
if (head == null)
return head;
ListNode newHead = head;
if (head.next != null) {
newHead = reverseList(head.next);
head.next.next = head;
head.next = null;
}
return newHead;
}
}
# python代码
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def reverseList(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
if not head:
return head
newHead = head
if head.next:
newHead = self.reverseList(head.next)
head.next.next = head
head.next = None
return newHead
# 复杂度分析
时间复杂度: 两种方法的时间复杂度都是O(n),其中n是链表的长度。
空间复杂度: 迭代法的空间复杂度是O(1),递归法涉及到保存调用栈的操作,调用栈最多n层,所以递归法的空间复杂度为O(n)。
上次更新: 2024/07/13, 23:38:01