环形链表
环形链表
题目链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/linked-list-cycle/
视频题解: https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV18z421q78k/
# LeetCode 141.环形链表
# 题目描述
给你一个链表的头节点 head ,判断链表中是否有环。
如果链表中有某个节点,可以通过连续跟踪 next 指针再次到达,则链表中存在环。 为了表示给定链表中的环,评测系统内部使用整数 pos 来表示链表尾连接到链表中的位置(索引从 0 开始)。注意:pos 不作为参数进行传递 。仅仅是为了标识链表的实际情况。
如果链表中存在环 ,则返回 true 。 否则,返回 false 。
举个例子:
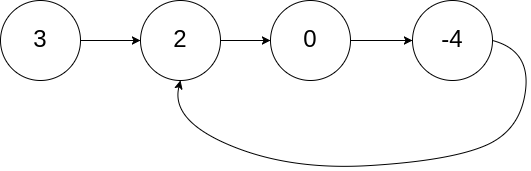
输入:head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1
输出:true
解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第二个节点。
# 视频讲解
建议大家点击视频跳转到b站环形链表 (opens new window)观看,体验更佳!
# 思路解析
# 方法一 使用hashset
使用一个hashset很容易判断链表是否有环,只需要一边遍历链表一边用hashset记录遍历过的节点,只要重复遍历到某个节点就说明链表存在环。
# C++代码
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
bool hasCycle(ListNode *head) {
if (!head)
return false;
unordered_set<ListNode*> visited;
ListNode* cur = head;
while (cur) {
//节点被访问过,说明有环
if (visited.find(cur) != visited.end()) {
return true;
}
//把节点存到visited
visited.emplace(cur);
cur = cur->next;
}
return false;
}
};
# java代码
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
if (head == null)
return false;
Set<ListNode> visited = new HashSet<>();
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
// 节点被访问过,说明有环
if (visited.contains(cur)) {
return true;
}
// 把节点存到visited
visited.add(cur);
cur = cur.next;
}
return false;
}
}
# python代码
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
class Solution:
def hasCycle(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> bool:
if not head:
return False
visited = set()
cur = head
while cur:
# 节点被访问过,说明有环
if cur in visited:
return True
# 把节点存到visited
visited.add(cur)
cur = cur.next
return False
# 方法二 快慢指针
定义两个指针slow和fast,一开始两个指针均指向链表头节点head,slow每次移动一步,fast每次移动两步。
- 如果链表不存在环,那么
fast指针会率先移动到NULL节点。 - 如果链表中存在环,
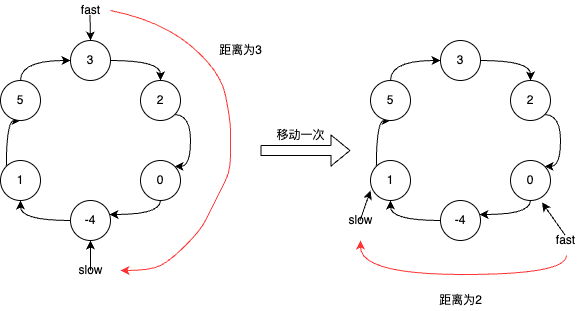
slow指针和fast指针最终都会进入到环里,这个时候两个指针的移动可以看成fast指针追slow指针。如下图,假设fast指针和slow指针在环中的距离为3,fast指针每次移动两步,slow指针每次移动一步,每次移动他们之间的距离就会缩小2 - 1 = 1,这样他们只需要移动3次就可以相遇。同理,如果fast指针和slow指针在环中的距离为n,只需要移动n次就可以相遇。
# C++代码
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
bool hasCycle(ListNode *head) {
ListNode* slow = head;
ListNode* fast = head;
while (fast && fast->next) {
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
//快指针和慢指针相遇说明有环
if (slow == fast) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
};
# java代码
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
// 快指针和慢指针相遇说明有环
if (slow == fast) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}
# python代码
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
class Solution:
def hasCycle(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> bool:
slow = head
fast = head
while fast and fast.next:
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next.next
# 快指针和慢指针相遇说明有环
if slow == fast:
return True
return False
# 复杂度分析
时间复杂度: 两种方法的时间复杂度都是O(n),其中n是链表的长度。
空间复杂度: 使用hashset的空间复杂度是O(n),快慢指针的空间复杂度是O(1)。
上次更新: 2024/07/25, 16:43:50