单词搜索 II
单词搜索 II
题目链接: https://leetcode.cn/problems/word-search-ii/
# LeetCode 212. 单词搜索 II
# 题目描述
给定一个 m x n 二维字符网格 board 和一个单词(字符串)列表 words, 返回所有二维网格上的单词 。
单词必须按照字母顺序,通过 相邻的单元格 内的字母构成,其中“相邻”单元格是那些水平相邻或垂直相邻的单元格。同一个单元格内的字母在一个单词中不允许被重复使用。
举个例子:
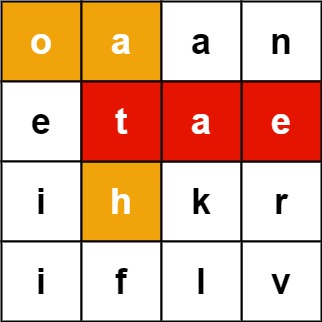
输入:board = [["o","a","a","n"],["e","t","a","e"],["i","h","k","r"],["i","f","l","v"]], words = ["oath","pea","eat","rain"]
输出:["eat","oath"]
# 思路解析
本题可以对前缀树稍加改造,用来保存给定的单词。
首先复习一下前缀树。
类似二叉树,首先需要定义出树的节点。二叉树最多只有两个孩子节点,二叉树的节点一般定义如下。
struct TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode *left;
TreeNode *right;
//这里忽略构造函数
};
这里的前缀树最多有26个孩子节点。在每个节点中,使用一个hash表来保存节点值与孩子节点之间的对应关系。前缀树节点定义如下。
struct TrieNode {
//字符和指向孩子节点指针的映射关系
unordered_map<char, TrieNode*> children;
//既可以用来判断当前节点是否为单词的结尾,又可以保存单词
string word;
//这里忽略构造函数
};
相比二叉树,前缀树节点的孩子节点比较多,而且前缀树节点中没有val值,其实它的val值可以通过父节点的children这个hash表推算出来,所以没有必要再增加一个val字段。
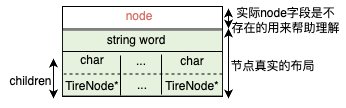
前缀树节点的结构如下图,图中的node字段在真实结构体中是不存在的,为了方便理解node相当于二叉树的val字段,弄清楚图中节点的布局是搞懂前缀树的关键。
由单词"a"生成的前缀树如下图。
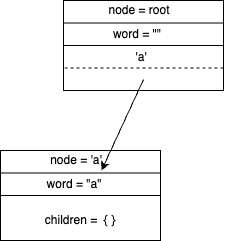
前缀树的根节点是没有类似二叉树val字段信息的,单词"a"中只有一个字符,生成的前缀树需要两个节点,孩子节点表示字符‘a’,孩子节点中的word字段不为空表示这个节点为单词“a”在前缀树中的最后一个节点。
单词搜索算法如下:
- 把给定的单词插入到上面定义的前缀树中。
void insert(string word) {
TrieNode* cur_node = this;
for (int i = 0; i < word.length(); ++i) {
if (cur_node->children.count(word[i]) == 0) {
//建立新节点和字符之间的映射关系
cur_node->children[word[i]] = new TrieNode();
}
cur_node = cur_node->children[word[i]];
}
cur_node->word = word;
}
- 深度优先搜索字符矩阵
board,一边搜索一边匹配前缀树。
void findWords_help(vector<vector<char>>& board, int row, int col, TrieNode* node, set<string>& res) {
//回溯条件
if (row < 0 || col < 0 || row >= board.size() || col >= board[0].size() || board[row][col] == '*' || !(node->children.count(board[row][col]))) {
return;
}
node = node->children[board[row][col]];
if (node->word != "" && !res.count(node->word)) {
//这里不能return,因为当前找到的单词有可能是另一个单词的前缀
res.emplace(node->word);
}
char c = board[row][col];
board[row][col] = '*';
//搜索前后左右相邻的字符
findWords_help(board, row - 1, col, node, res);
findWords_help(board, row + 1, col, node, res);
findWords_help(board, row, col - 1, node, res);
findWords_help(board, row, col + 1, node, res);
board[row][col] = c;
}
# C++代码
struct TrieNode {
//字符和指向孩子节点指针的映射关系
unordered_map<char, TrieNode*> children;
//既可以用来判断当前节点是否为单词的结尾,又可以保存单词
string word;
TrieNode() {
word = "";
}
void insert(string word) {
TrieNode* cur_node = this;
for (int i = 0; i < word.length(); ++i) {
if (cur_node->children.count(word[i]) == 0) {
//建立新节点和字符之间的映射关系
cur_node->children[word[i]] = new TrieNode();
}
cur_node = cur_node->children[word[i]];
}
cur_node->word = word;
}
};
class Solution {
public:
vector<string> findWords(vector<vector<char>>& board, vector<string>& words) {
TrieNode* root = new TrieNode();
//根据给定的单词构造前缀树
for (int i = 0; i < words.size(); ++i) {
root->insert(words[i]);
}
vector<string> res;
//使用set是为了对结果去重
set<string> tmp_res;
for (int row = 0; row < board.size(); ++row) {
for (int col = 0; col < board[0].size(); ++col) { //矩阵的每一个元素做为起点开始搜索
findWords_help(board, row, col, root, tmp_res);
}
}
for (auto str : tmp_res) {
res.push_back(str);
}
return res;
}
void findWords_help(vector<vector<char>>& board, int row, int col, TrieNode* node, set<string>& res) {
//回溯条件
if (row < 0 || col < 0 || row >= board.size() || col >= board[0].size() || board[row][col] == '*' || !(node->children.count(board[row][col]))) {
return;
}
node = node->children[board[row][col]];
if (node->word != "" && !res.count(node->word)) {
//这里不能return,因为当前找到的单词有可能是另一个单词的前缀
res.emplace(node->word);
}
char c = board[row][col];
board[row][col] = '*';
//搜索前后左右相邻的字符
findWords_help(board, row - 1, col, node, res);
findWords_help(board, row + 1, col, node, res);
findWords_help(board, row, col - 1, node, res);
findWords_help(board, row, col + 1, node, res);
board[row][col] = c;
}
};
# 复杂度分析
时间复杂度: 因为这棵前缀树为四叉树树,时间复杂度为O(mnt4t-1),其中m为board的行数,n为board的列数,t为最长单词的长度,4t-1是前缀树的叶子数,即一棵树最大搜索路径数。
空间复杂度: 空间复杂度跟前缀树的总节点数相关。
上次更新: 2024/07/08, 20:31:33